Diagnostic cardiac catheterization is the procedure of inserting catheters, which are hollow plastic tubes with a diameter of 2 to 3 mm, into veins and/or arteries in the neck, leg, or arm, and then advancing them to the right and left sides of the heart. The pressure of the blood in various chambers of the heart can be measured, blood samples can be obtained, and dye (radiographic contrast material) can be injected to provide x-ray visualisation once the catheters are positioned in the various heart chambers or blood channels.
OXYMETRY AND PRESSURE STUDY
Materials Needed
For Every Paediatric Procedures
Paediatric Instrument Tray
5cc Luerlock syringe – 2
10cc Luerlock syringe – 1
3-way stopcock – 2
2cc syringer – 10
Swan Ganz Catheter
Preparation for Diagnostic Cardiac Catheterization
- After sterile scrubbing, gowning and gloving, clean the inguinal region of both sides (from umbilicus to knee joint). Drape the patient (expose both the groins in a single side hole).
- Load local Anesthesia in 5cc Luerlock syringe (30 mg/kg) and change the needle. Then load heparin in a 2cc syringe (100 IU/kg)
- Flush the center port of Swan-Ganz catheter with heparinized saline. Dip the tip of the catheter in saline and check the balloon by inflating it with of air. The Inflation Air may vary depends on French size of Swan-Ganz
- Flush the sheath & puncture needle
Procedure steps for Diagnostic Cardiac Catheterization
Step 1: Getting venous access & indwelling 6F sheath, introduce Swan-Ganz catheter & inflate the balloon once it passes the sheath.

Step 2: Advance the catheter till it reaches IVC to RA to PA to Pulmonary capillary wedge pressure
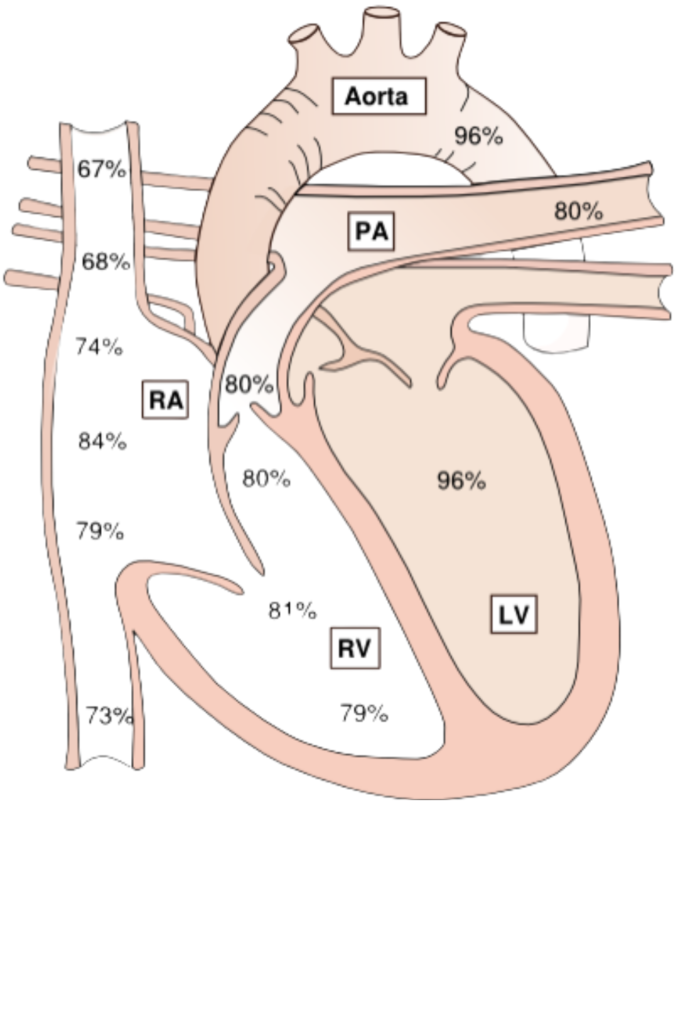
Step 3: When the catheter is in PA perform an oxygen saturation study
Step 4: Take samples from PA, RV, RA, and SVC and IVC
Pressure study should be done from following Chambers
a. RA pressure (phasic and mean), Measuring Scale 40
b. RV pressure (phasic only), Measuring Scale 40 or 100
c. PCW (phasic and mean), Measuring Scale 40
d. PCW to PA pullback pressure (mean PCW to Pull back), Measuring Scale 40
e. PA pressure (systolic and diastolic, mean), Measuring Scale 40
Step 5: Expel air, label the sample and sent it to lab. Withdraw the catheter after the balloon deflation
Step 6: Flush the sheath catheter and remove the sheath, apply pressure for 10 mins
Step 7:Apply tight bandage and assess the patency of distal pulse.